NATO’s evolution: In today’s rapidly changing global landscape, the role of NATO in international politics has never been more vital. With the rise of new security challenges and the evolving nature of warfare, NATO has continuously adapted to safeguard the collective defense and security of its member states. This article delves into the history and evolution of NATO, from its inception in 1949 to its current prominence in global affairs.
The formation and early years of NATO
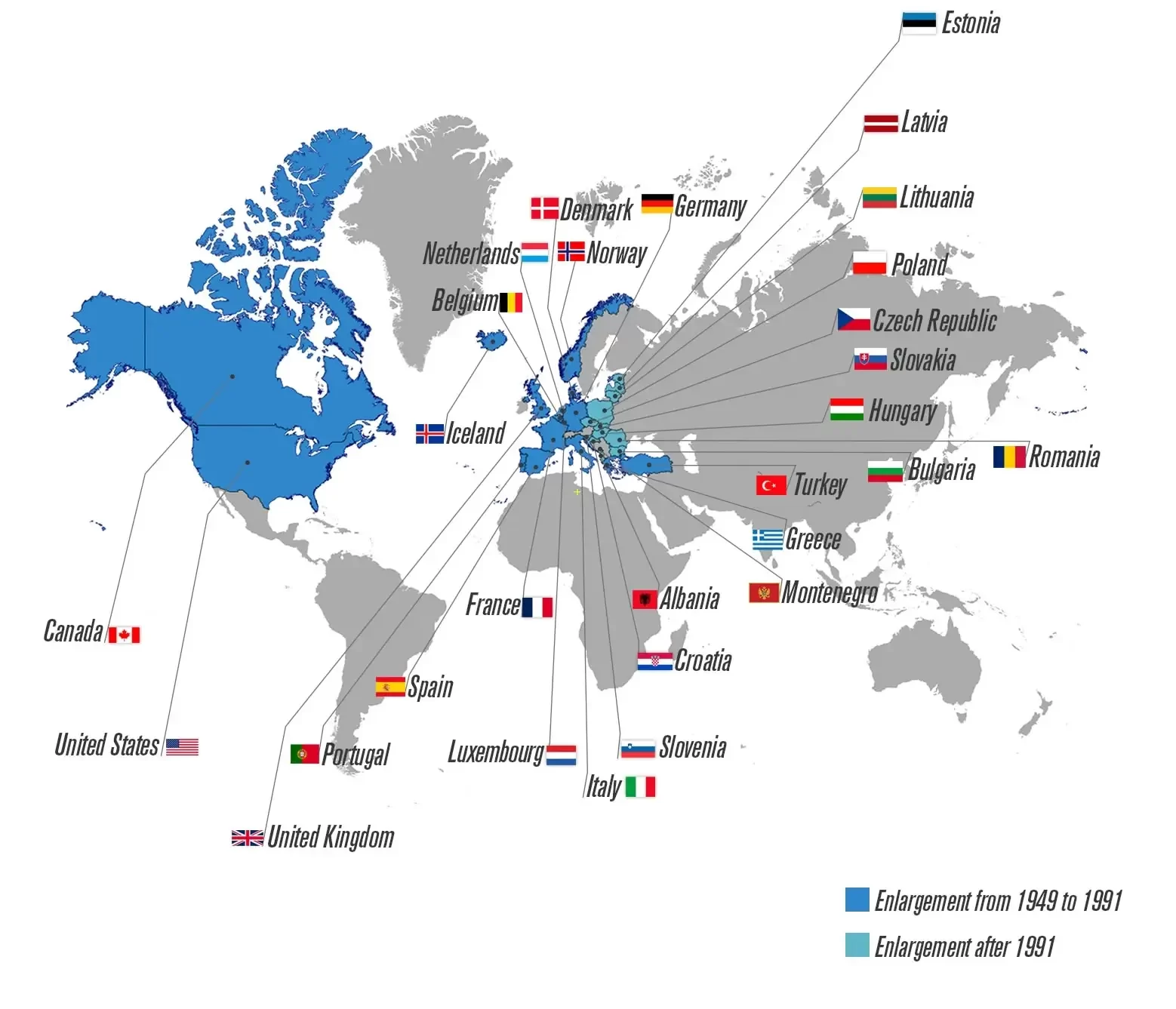
NATO, short for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, was formed in 1949 as a response to the growing threat of the Soviet Union. The alliance initially consisted of twelve member states, including the United States, Canada, and several Western European countries. The creation of NATO was seen as a necessary step to counter the Soviet Union’s expansionist ambitions and ensure the security of its member states.
During its early years, NATO focused primarily on collective defense and military cooperation. It established a system of mutual defense, which meant that an attack on one member state would be considered an attack on all. This principle served as a powerful deterrent against potential aggression from the Soviet Union and provided a sense of security for the member states. NATO also developed a command structure and conducted joint military exercises to enhance coordination and interoperability among its members.
The Cold War and NATO’s role
The Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union dominated much of the twentieth century and greatly influenced NATO’s role and activities. NATO served as a crucial pillar of Western defense strategy during this period, providing a unified front against the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact. The alliance played a significant role in deterring aggression and maintaining stability in Europe.
NATO’s collective defense commitment was put to the test during the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962. The alliance stood firm in support of the United States and demonstrated its resolve in the face of a potentially catastrophic nuclear showdown. This event showcased NATO’s ability to effectively respond to emerging threats and maintain peace and security.
Post-Cold War changes in NATO
The end of the Cold War in the early 1990s brought about significant changes in NATO’s purpose and objectives. With the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the alliance faced a new geopolitical landscape and had to redefine its role in a post-Cold War world. NATO began to shift its focus from collective defense against a conventional military threat to addressing new security challenges, such as terrorism, regional conflicts, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
One of the key milestones during this period was the adoption of the Strategic Concept in 1991, which outlined NATO’s new strategic priorities. The concept emphasized the importance of crisis management, conflict prevention, and cooperative security. NATO also started to engage in peacekeeping operations, particularly in the Balkans, where it played a crucial role in ending the conflicts in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, and Macedonia.
NATO’s expansion and partnerships
As the security landscape continued to evolve, NATO embarked on a process of expansion to ensure stability and security in Europe. Several countries from Central and Eastern Europe, including Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, joined NATO in 1999. This enlargement was seen as a symbol of NATO’s commitment to the principles of democracy, freedom, and collective security.
In addition to enlargement, NATO also developed partnerships with non-member states, aiming to enhance cooperation and promote security in the Euro-Atlantic region and beyond. These partnerships, such as the Partnership for Peace program, allowed NATO to work closely with countries that shared common security interests. NATO’s partnerships have been instrumental in fostering stability, promoting democratic reforms, and strengthening the rule of law in partner countries.

NATO’s role in counterterrorism efforts
The terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, marked a turning point in NATO’s role in global security. In response to these attacks, NATO invoked Article 5 of the Washington Treaty for the first time, declaring that the attacks on the United States were considered an attack on all NATO members. This solidified NATO’s commitment to collective defense in the face of non-traditional security threats.
Following the invocation of Article 5, NATO took a leading role in the fight against terrorism. The alliance established the NATO Response Force, a highly capable and rapidly deployable multinational force, to support counterterrorism efforts. NATO also deployed troops to Afghanistan in support of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF), playing a critical role in stabilizing the country and combating terrorist groups such as Al-Qaeda.
NATO’s involvement in humanitarian and peacekeeping missions
Apart from its core mission of collective defense, NATO has been actively engaged in humanitarian and peacekeeping missions around the world. The alliance has played a crucial role in promoting stability and democracy in conflict-ridden regions, particularly in the Balkans.
In the 1990s, NATO intervened in the conflicts in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, and Macedonia to end the violence and establish a lasting peace. The alliance’s involvement helped prevent further atrocities and provided support for post-conflict reconstruction and institution-building. NATO’s peacekeeping missions have also extended beyond Europe, with the alliance contributing to peacekeeping efforts in Afghanistan and supporting the African Union’s peacekeeping mission in Darfur, Sudan.
Challenges and criticisms of NATO
While NATO has been successful in adapting to changing security challenges, it has also faced a range of challenges and criticisms. One of the main challenges is the burden-sharing issue among member states. Defense spending varies significantly among NATO members, with some countries failing to meet the agreed-upon target of spending 2% of their GDP on defense. This has led to concerns about the alliance’s overall effectiveness and burden falling disproportionately on a few countries.
NATO has also faced criticism for its interventions and military actions, particularly in the aftermath of the Iraq War. Some argue that NATO’s involvement in conflicts outside of its traditional area of operations has strained its resources and diverted attention from its core mission of collective defense. Additionally, NATO’s partnerships with countries that have questionable human rights records have raised concerns about the alliance’s commitment to its fundamental values.
The future of NATO in a changing world
As the world continues to evolve, NATO faces new challenges and opportunities. The rise of new global powers, advancements in technology, and the changing nature of warfare require NATO to adapt and remain relevant in the twenty-first century.
NATO’s future lies in its ability to maintain a strong, cohesive alliance, adapt its capabilities to address emerging threats, and deepen partnerships with like-minded countries and organizations. The alliance must continue to invest in cutting-edge technologies, such as cyber defense and space capabilities, to effectively counter new security challenges. Moreover, NATO must ensure that its actions are in line with its core values of democracy, human rights, and the rule of law, while also addressing the concerns and criticisms raised by its member states and partners.

Conclusion
NATO has come a long way since its formation in 1949. From its early years as a collective defense alliance against the Soviet Union to its current role in addressing new security challenges, NATO has proven its adaptability and resilience. The alliance’s contributions to collective defense, crisis management, and peacekeeping have been crucial in promoting stability and security in a rapidly changing world.
As we navigate the complexities of today’s global politics, understanding the evolution and significance of NATO is essential. By delving into the history and impact of this influential organization, we gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. NATO’s ability to adapt, innovate, and maintain effective deterrence will be vital in ensuring a peaceful and secure future for its member states and the international community as a whole.
If you found this article insightful and wish to delve deeper into the historical contexts that have shaped our current geopolitical landscape, we highly encourage you to read our article on the Fall of the USSR. It offers a compelling look at one of the pivotal moments in history that has had a lasting impact on global affairs, including the strategic responses and adaptations of organizations like NATO.



